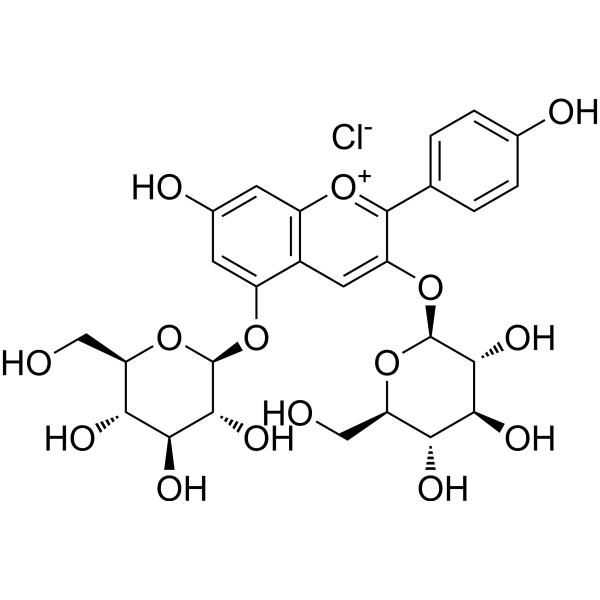
Pelargonidin-3,5-O-diglucoside chloride
CAS No. 17334-58-6
Pelargonidin-3,5-O-diglucoside chloride( —— )
Catalog No. M31224 CAS No. 17334-58-6
Pelargonidin-3,5-O-diglucoside chloride has antioxidant activity.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 5MG | 639 | In Stock |


|
| 50MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
| 100MG | Get Quote | In Stock |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NamePelargonidin-3,5-O-diglucoside chloride
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionPelargonidin-3,5-O-diglucoside chloride has antioxidant activity.
-
DescriptionPelargonidin-3,5-O-diglucoside chloride has antioxidant activity.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
Recptor——
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number17334-58-6
-
Formula Weight631
-
Molecular FormulaC27H31O15Cl
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILES——
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Oleuropeinic acid
Oleuropeinic acid is present initially in olive tissues or formed by the thermal treatment, possibly by the oxidation of oleuropein. Oleuropeinic acid is an antioxidant-soluble fiber.
-
4-Hydroxy-3-Nitroben...
4-Hydroxy-3-Nitrobenzyl Alcohol is a marine derived natural products found in Phidolopora pacifica.
-
Glimepiride sulfonam...
Glimepiride sulfonamide is an antiinflammatory agent.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


